Step-by-Step Instructions for Forcing the Closure of Unresponsive Programs in Windows 10

Step-by-Step Instructions for Forcing the Closure of Unresponsive Programs in Windows 10
Quick Links
Key Takeaways
- Try pressing Alt+F4 to force-close an app.
- Open Task Manager, select the frozen app, and click “End Task” to force quit it.
- Run “tasklist” in Command Prompt find tasks, and then use “taskkill /im
.exe” to force quit the app.
It’s not uncommon for an application to stop responding on Windows 10. When it happens, you can force the app to shut down, effectively unfreezing said application. Here’s how to force quit an app on Windows 10.
Try a Keyboard Shortcut
It’s frustrating when an app you’re using suddenly freezes. We’ve all done it—exasperatingly clicking the “X” button at least 20 times to close the frozen program. There’s a better way.
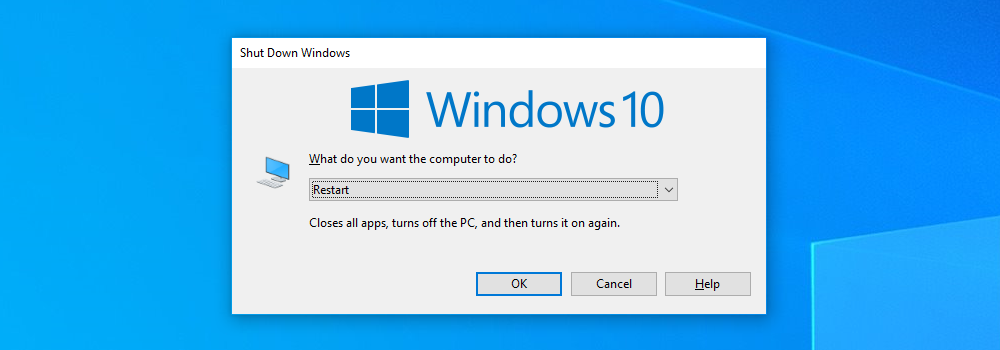
With the frozen application in focus, press Alt+F4 on your keyboard to close it. If the Windows desktop is in focus instead, you’ll see a “Shut Down Windows” prompt instead.
This won’t always work—some frozen applications just won’t respond.
Force Quit Using Task Manager
As the name implies, Task Manager is a tool that shows which apps are currently running (as well as other information like resource usage and process stats) and allows you to manage them appropriately.
To open Task Manager , you can press Ctrl+Shift+Esc on your keyboard or right-click the Windows task bar and select “Task Manager” from the menu.
With Task Manager open, select the task you want to force quit and then select “End Task.”
If you don’t see the name of the app in the list here, click “More Details” and find it in the list on the Processes tab.
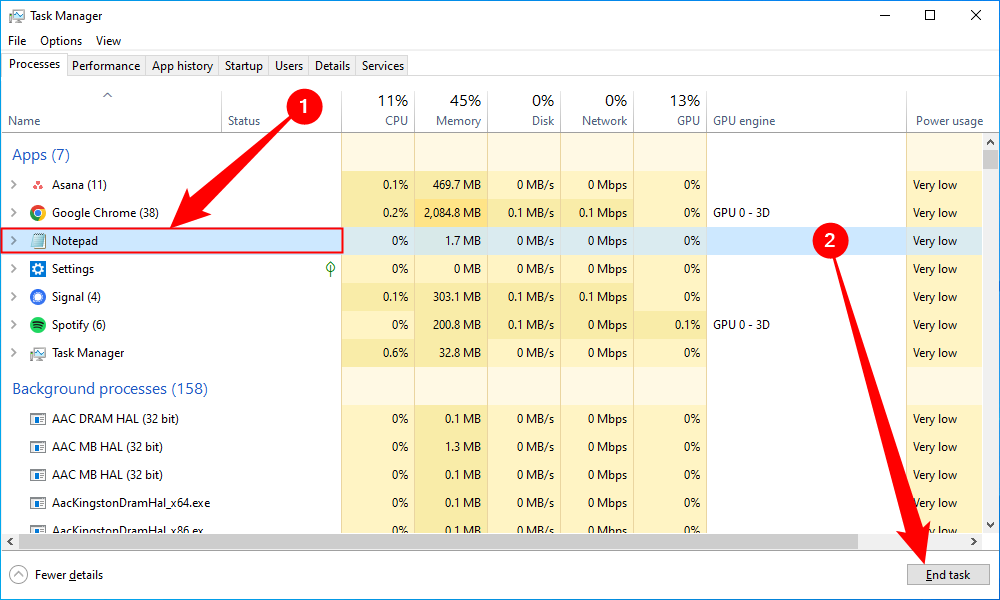
The frozen program will now close.
Force Quit an App Using Command Prompt
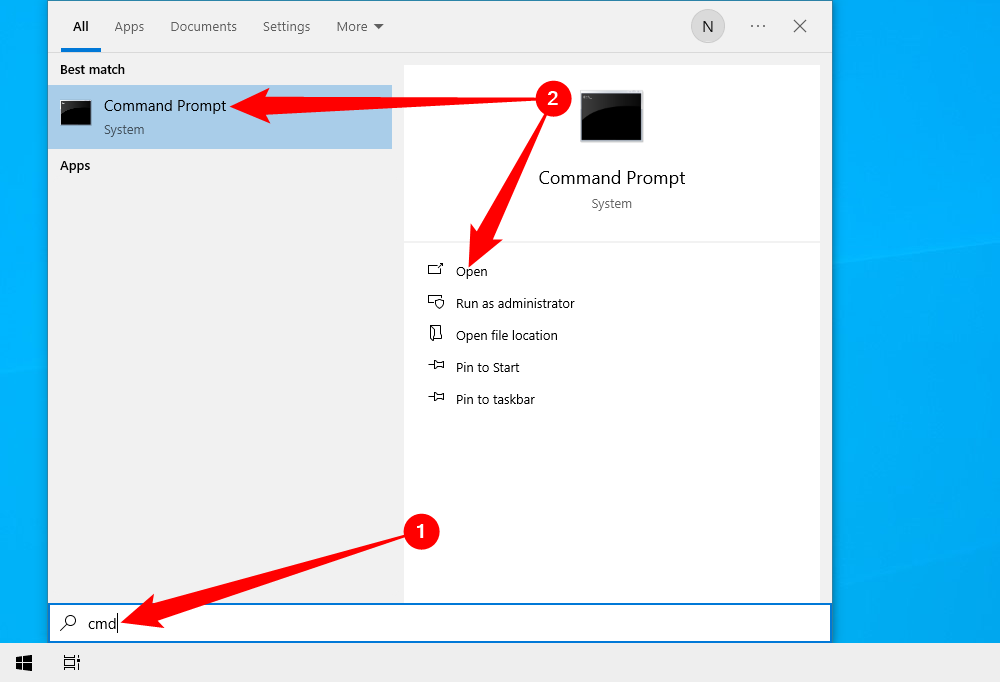
You can find and force quit tasks from the Command Prompt. Open Command Prompt by typing cmd in the Windows search bar, and then selecting the “Command Prompt” app from the search results.
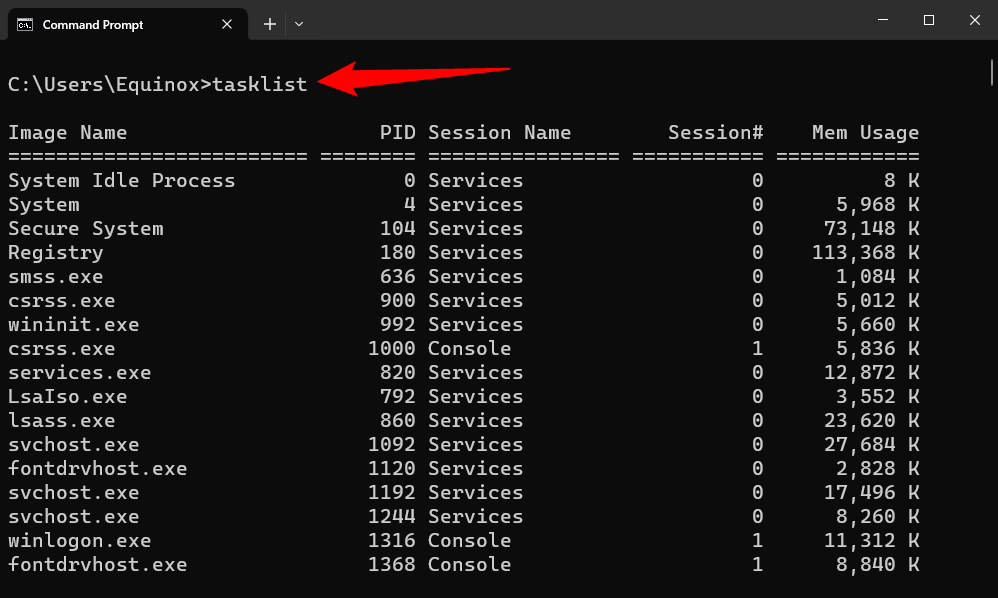
In Command Prompt, type tasklist and press “Enter.” Once executed, Command Prompt will display a list of currently running programs, services, and tasks.
The list can admittedly be a bit overwhelming, so just remember to append .exe to the end of the program name. Once you’re ready to force quit the program, execute this command:
taskkill /im
So, if I wanted to force quit Notepad, I’d run this command:
taskkill /im notepad.exe
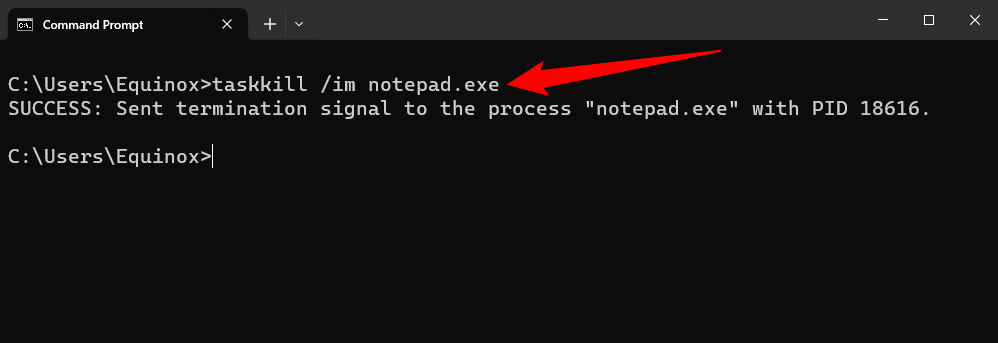
A success message will be returned, letting you know you’ve successfully force quit the problematic application.
Of course, you can always reboot or shut down your PC to close an app that’s really stuck.
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved Ultimate Guide Top 10 High-Quality, No-Cost Recording Tools
- [SOLVED] uTorrent Slow Download Speed
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Elite Camera Selection Our Top 15 Picks
- [Updated] In 2024, Innovation at Play The Best Professional 360-Degree Cameras - 2023 Update
- 2024 Approved Outsmarting Online Advertising on Social Network Sites
- 2024 Approved Record Rapidly Innovative iPhone Time-Lapse Methods
- Comprimere I Video Di Grandi Dimensioni per WhatsApp, Mantenendo La Qualità Ottimale Con WinXDVD
- Dragon's Dogma 2 PC Crashes - Easy Fixes to Enjoy Uninterrupted Gaming
- Genetic Variations in the Cytochrome P45amoeba Methylene Blue Enzymes May Lead to Slower or Faster Clearance of Drugs, Impacting Their Efficacy and Potential for Harm
- Google Wireless Nest Doorbell Review - Does It Live Up to Expectations on Batteries?
- How to Prevent and Repair Crashes in Cities: Skylines 2 on Your PC - Comprehensive Guide
- How To Stop Sea of Thieves From Crashing on PlayStation and PC
- Stunning Beach Wallsavers & Image Banks - Quality Visuals From YL Software
- Winning the Battle Againnst Blender PC Instability - Solutions Proven Effective!
- Title: Step-by-Step Instructions for Forcing the Closure of Unresponsive Programs in Windows 10
- Author: Christopher
- Created at : 2024-12-08 18:12:26
- Updated at : 2024-12-12 16:14:34
- Link: https://win-blog.techidaily.com/step-by-step-instructions-for-forcing-the-closure-of-unresponsive-programs-in-windows-10/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.