
Transforming Lengthy Excel Columns Into Multiple Segments - A Comprehensive Tutorial

Transforming Lengthy Excel Columns Into Multiple Segments - A Comprehensive Tutorial
Quick Links
Too much data in a single column can make your Microsoft Excel spreadsheet harder to read. To improve it, you should consider splitting up your column using the “Text to Columns” or “Flash Fill” features.
“Text to Columns” will replace your single column with multiple columns using the same data. “Flash Fill” will replicate the data, splitting it into new, individual columns while leaving the original column intact.
How to Use Text to Columns in Excel
Microsoft Excel includes a special feature that allows you to split up extra long columns. It does this by separating columns using delimiters, like commas or semicolons, which split up the data.
The feature works by using Text to Columns , which you can access from the “Data” tab in your Microsoft Excel ribbon bar.
Related: How to Use Text to Columns Like an Excel Pro
To test this feature, we’ll be using a set of data (an employee list, showing names, dates of birth, and other information) in a single column. Each section of data is in a single cell, separated by a semicolon.
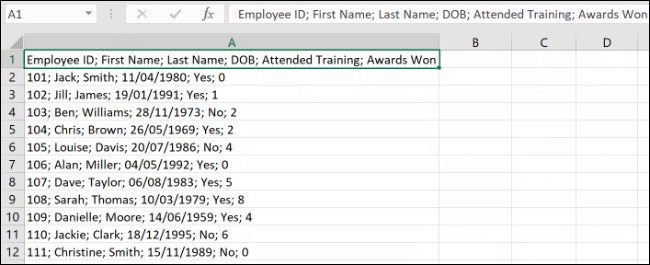
You’ll need to select the cells containing your data first (cells A1 to A12 in the example above).
From Excel’s “Data” tab, click the “Text to Columns” button found in the “Data Tools” section.
This will bring up the “Convert Text to Columns Wizard” window and allows you to begin separating your data. From the options, select the “Delimited” radio button and click “Next” to continue.
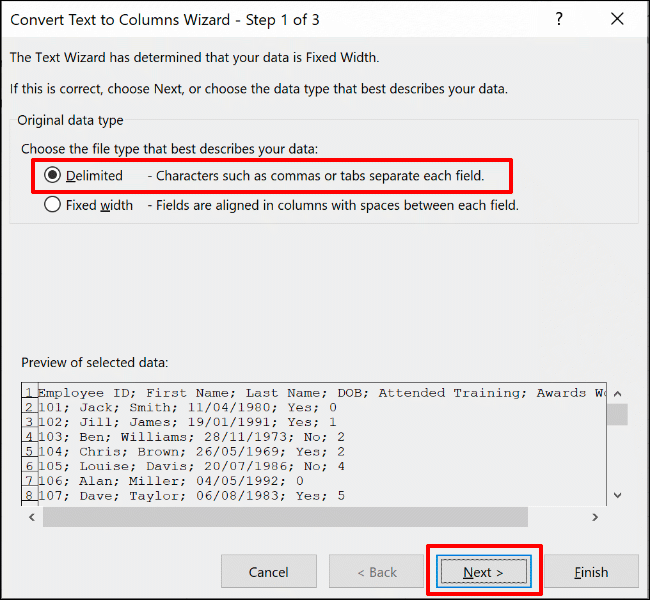
By default, Excel will choose to try and separate your single column data by each tab it finds. This is fine, but for our example, we’re using data that’s separated by semicolons.
Choose your delimiter option from the side menu. For our example, our chosen delimiter is a semicolon.
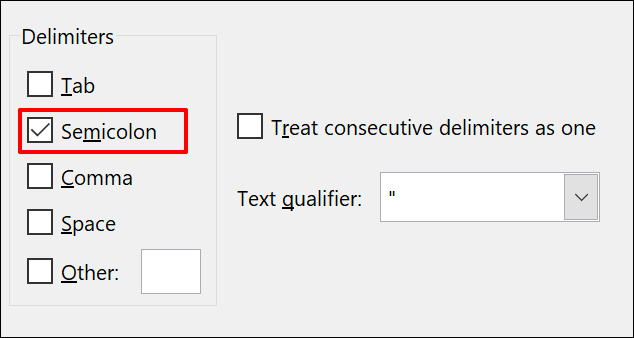
You can see how the converted data will look in the “Data Preview” section at the bottom of the menu.
Once you’re ready, click “Next” to continue.
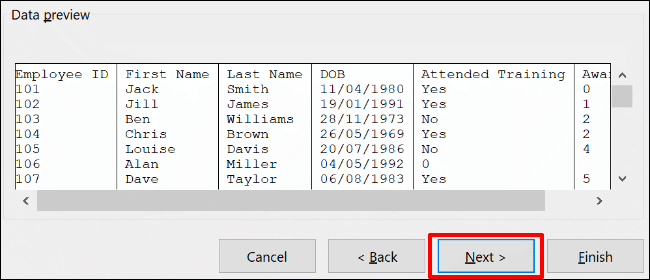
You’ll now need to set the cell types for each column. For instance, if you have a column with dates, you can set the appropriate date format for that column. By default, each column will be set to the “General” setting.
Using this option, Excel will attempt to set the data type for each column automatically. To set these manually, click on your column in the “Data Preview” section first. From there, select the appropriate data type from the “Column Data Format” section.
If you want to skip a column completely, select your column, then choose the “Do Not Import Column (Skip)” option. Click “Finish” to begin the conversion.
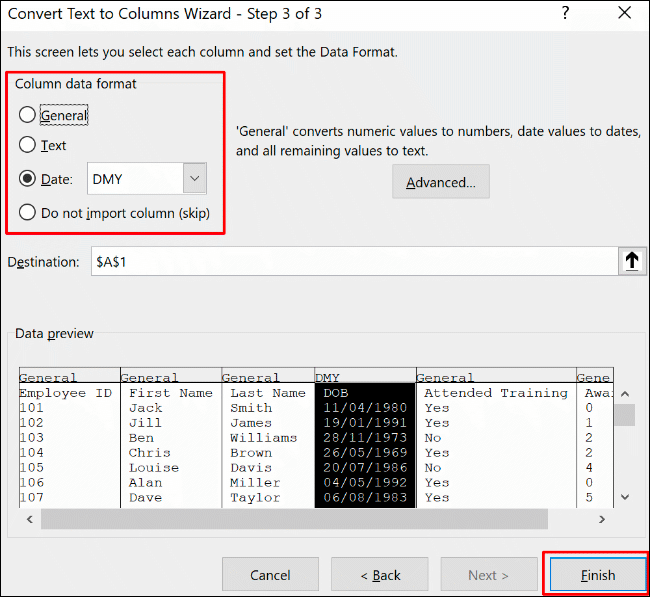
Your single column will separate each section, using the delimiters, into individual columns using the cell formatting options you selected.
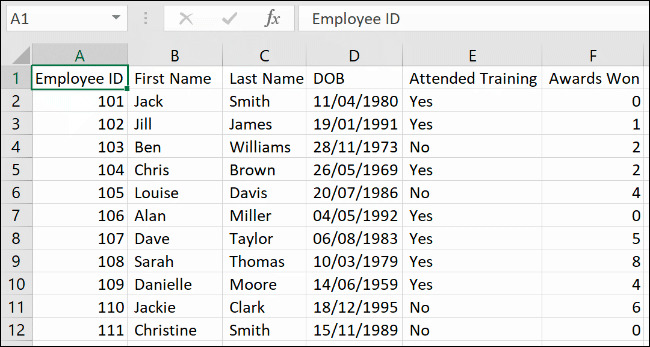
How to Use Flash Fill in Excel
If you’d like to keep your original data intact, but still separate the data, you can use the “Flash Fill” feature instead.
Using our employee list example, we have a single column (column A) header row, with a semicolon delimiter separating each bit of data.
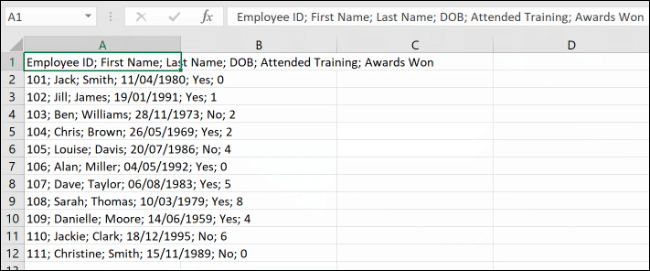
To use the “Flash Fill” feature, start by typing out the column headers in row 1. For our example, “Employee ID” would go in cell B1, “First Name” in cell C1, etc.
For each column, select your header row. Start with B1 (the “Employee ID” header in this example) and then, in the “Data Tools” section of the “Data” tab, click the “Flash Fill” button.
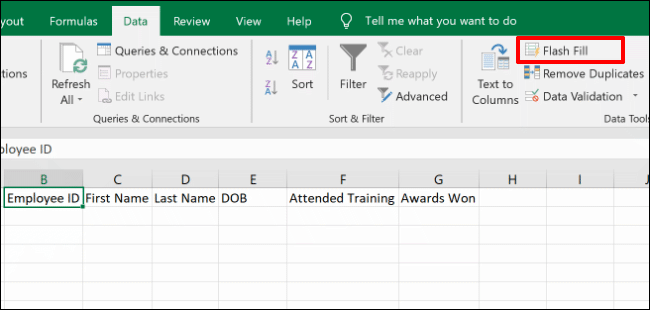
Repeat the action for each of your header cells (C1, D1, etc) to automatically fill the new columns with the matching data.
If the data is formatted correctly in your original column, Excel will automatically separate the content using the original header cell (A1) as its guide. If you receive an error, type the following value in the sequence in the cell below your header cell, then click the “Flash Fill” button again.
In our example, that would be the first data example in cell B2 (“101”) after the header cell in B1 (“Employee ID”).
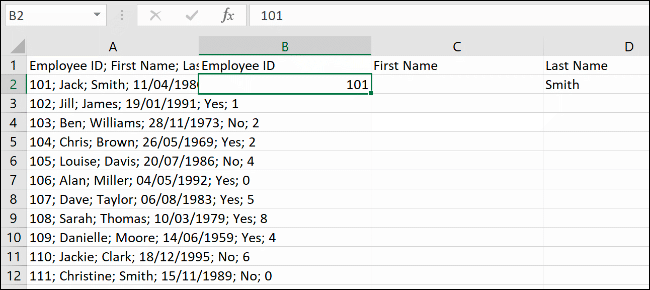
Each new column will fill with the data from the original column, using the initial first or second rows as the guide to choose the correct data.

In the example above, the long column (column A) has been separated into six new columns (B to G).
Because the layout of rows 1 to 12 is the same, the “Flash Fill” feature is able to copy and separate the data, using the header row and first bit of data.
Also read:
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Accessing Global Events Facebook Live on Roku Devices
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Ideal Websites for Painless JPEG to GIF Changeover
- Behebt Die Fehlerbehebung Von Windows Amoynebzbk: Die Sicherungsgröße Wird Mit Null Byte Aufgeführt
- Fix Your GTA Ve's FPS Drop: Rapid and Simple Methods to Improve Performance
- How to Resolve the Problem of Resident Evil Village Not Starting Properly
- How to Unlock Xiaomi Redmi A2+ Phone with Broken Screen
- Latest Updates on Apple's Electric Vehicle: Pricing Details & Launch Timeline Revealed!
- Solutions for Restarting a Frozen Microsoft IE Browser
- Step-by-Step: Quick Remedies to Your Discord JavaScript Glitches
- Tips to Boost Frames Per Second in 'Avatar: The Game - Frontiers of Pandora'
- Title: Transforming Lengthy Excel Columns Into Multiple Segments - A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Author: Christopher
- Created at : 2024-12-08 17:19:51
- Updated at : 2024-12-12 18:28:49
- Link: https://win-blog.techidaily.com/transforming-lengthy-excel-columns-into-multiple-segments-a-comprehensive-tutorial/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.